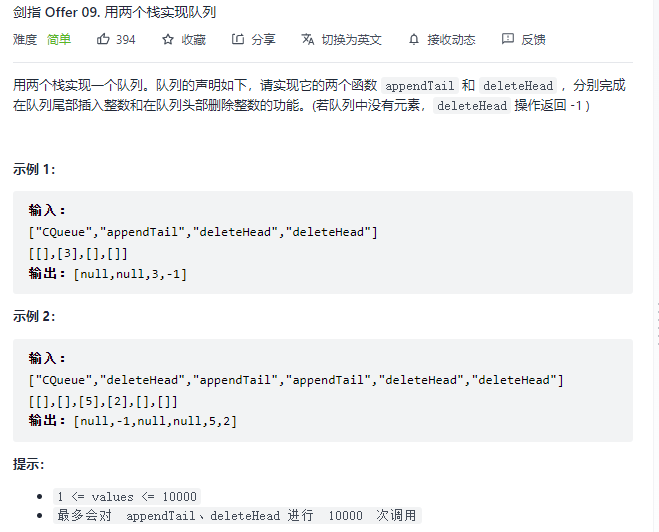
两个栈实现一个队列
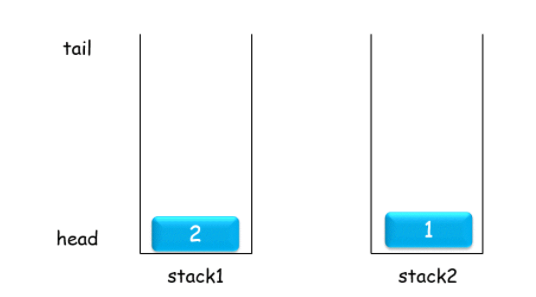
两个栈实现一个队列,把两个栈看成一个U型队列,stack1队尾那一部分,因此append之间往stack1里面push即可,而stack2是队头那一部分,stack2最上面的即是队列头,因此deletehead只须对stack2执行pop即可。
但是如果stack2是空的怎么办?应该要从stack1那里取一部分放到stack2里面即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class CQueue {
public:
stack<int>s1;
stack<int>s2;
CQueue() {
while(!s1.empty()){
s1.pop();
}
while(!s2.empty()){
s2.pop();
}
}
void appendTail(int value) {
s1.push(value);
}
int deleteHead() {
if(s2.empty()){
while(!s1.empty()){
s2.push(s1.top());
s1.pop();
}
}
if(s2.empty())return -1;
int ans = s2.top();
s2.pop();
return ans;
}
};
|
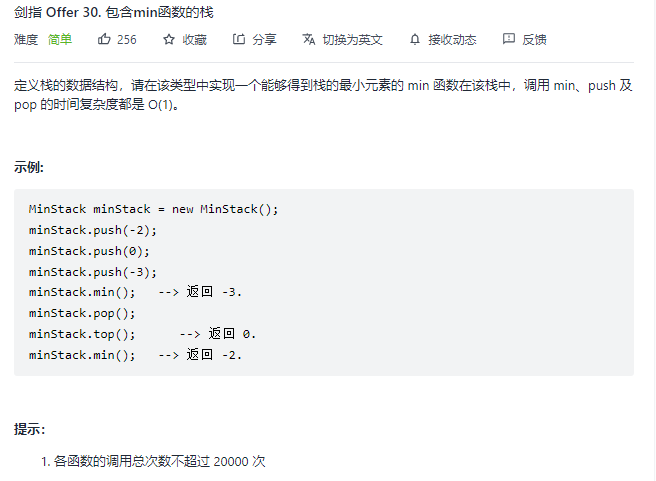
包含min函数的栈
这个需要另一个辅助栈用于存储最小值即可。
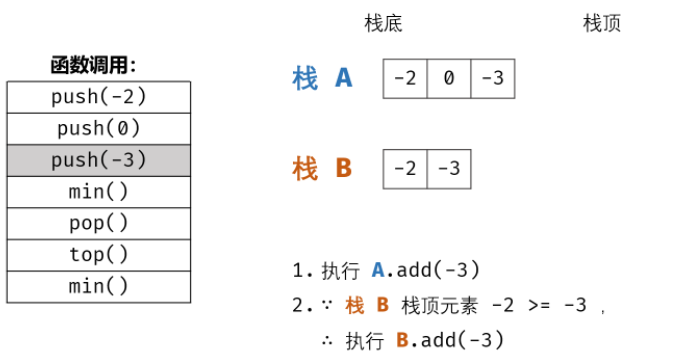
主要在于push操作的时候进行判断,如果minx的值发生变化(注意如果当前push的值x等于minx,栈B也要更新),那么就往栈B里面将minx存入。
而pop操作同样进行一次判断,如果栈A.top()==栈B.top(),将两个一起弹出即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| class MinStack {
public:
stack<int>s;
stack<int>mins;
int minx;
MinStack() {
while(!s.empty()){
s.pop();
}
while(!mins.empty()){
mins.pop();
}
minx = INT_MAX;
}
void push(int x) {
s.push(x);
if(x<=minx){
minx=x;
mins.push(x);
}
}
void pop() {
if(s.top()==mins.top()){
mins.pop();
s.pop();
if(!mins.empty())minx=mins.top();
else minx = INT_MAX;
}
else s.pop();
}
int top() {
return s.top();
}
int min() {
return minx;
}
};
|
用一个或两个队列实现一个栈

两个队列实现一个栈
这个的核心思想在于对于每个进入的新元素x,都要将x前的元素移入另一个队列再从另一个队列移回来,这样队列里的每一个元素都变为倒序存储了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| class MyStack {
public:
queue<int>q1;
queue<int>q2;
MyStack() {
while(!q1.empty())q1.pop();
while(!q2.empty())q2.pop();
}
void push(int x) {
if(q1.empty())q1.push(x);
else{
while(!q1.empty()){
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
q1.push(x);
while(!q2.empty()){
q1.push(q2.front());
q2.pop();
}
}
}
int pop() {
int a = q1.front();
q1.pop();
return a;
}
int top() {
return q1.front();
}
bool empty() {
return q1.empty();
}
};
|
一个队列实现一个栈
两个队列实现一个栈核心思想在于对于每个新插入的新元素x,都要将x前的元素移入另一个队列再从另一个队列移回来,这样队列里的每一个元素都变为倒序存储了。
而稍微修改一下思路,将新插入x前的元素直接移到x的后面即可了。无非就是循环地执行pop操作,再执行push操作即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class MyStack {
public:
queue<int>q1;
MyStack() {
while(!q1.empty())q1.pop();
}
void push(int x) {
int size = q1.size();
q1.push(x);
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
q1.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
}
int pop() {
int a = q1.front();
q1.pop();
return a;
}
int top() {
return q1.front();
}
bool empty() {
return q1.empty();
}
};
|